Buried pipeline detection technology scheme (2) - pipeline detector
Pipeline detection technology scheme (2) - pipeline detector detection method
(A) pipeline instrument detection principle
Metal pipeline generally has a medium strength of magnetic (K value is generally 100×4π×SI ~ 1000×10-6×4π×SI), its resistivity is generally 0.23×10-4ΩM ~ 0.89×10-4ΩM, with good electrical conductivity, magnetic conductivity. The underground pipeline is generally laid in the shallow soil layer within 5 meters below the surface, the surface soil layer is generally non-magnetic, and its resistivity is several ohms to dozens of ohms, which shows that there are obvious electrical and magnetic differences between the underground pipeline and the surrounding medium. Therefore, the underground pipeline detector made by the principle of electromagnetic induction can find out the distribution of underground metal pipelines more correctly, and has the necessary geophysical prerequisite for detection.
(2) Detection methods
When an alternating electromagnetic field of a certain frequency and appropriate intensity is applied to the target pipeline, a corresponding alternating current will pass between the target pipeline and the earth, and the alternating current will generate an alternating electromagnetic field of the same frequency in the surrounding space, that is, a secondary alternating electromagnetic field anomaly will be formed around the target pipeline, and the location of the target pipeline can be determined by detecting the anomaly with a receiving device. To achieve the purpose of detecting underground pipelines. The detection methods are divided into active source method and passive source method, and the active source method includes direct connection method, clamp method and induction method.
1. Direct connection method
The main use of underground pipeline outcrop. Such as: valves, manhole, all kinds of watch boxes and other detection of metal pipelines. Method principle: One end of the transmitter is connected to the target pipeline, the other end is grounded, the signal is directly added to the target pipeline by the transmitter, and the signal is received by the receiver and the signal characteristics are analyzed, that is, the location of the underground pipeline can be determined. Mainly used for steel pipe, cast iron pipe, metal wire and other metal pipelines.


2. Induction method
According to the principle of electromagnetic induction, a transmitting coil with alternating current is placed above (or near) the metal pipeline, and the coil is subjected to the action of alternating current to generate an alternating electromagnetic field and propagate to the surrounding area, which is called "primary field". Because the size and direction of the "primary field" magnetic flux through the metal pipeline are constantly changing, the metal pipeline generates an induced current, and its size is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux, and the frequency is the same as the "primary field". Similarly, the induced current generates an induced electromagnetic field of the same frequency around it, that is, a "secondary field". By receiving the "secondary field" signal at a certain distance and analyzing its distribution characteristics, the purpose of finding the underground metal pipeline is achieved
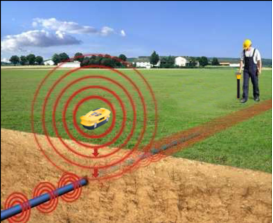

3. Clamp method
Using the clamp equipped with the special underground pipeline detector, the clamp is set on the metal pipe line, and the signal is directly added to the target pipeline through the induction coil on the clamp, and the receiver receives the signal and analyzes its distribution characteristics, that is, the location of the underground pipeline can be determined, which is mainly used for some communication pipelines such as cables and optical cables.



 Hotline
Hotline

